簡介
The wattmeter, a commonly used electrical measurement instrument, is employed for assessing power in alternating current circuits. It accurately measures parameters such as voltage, current, and power factor while offering power calculation and display capabilities. Its significance extends to power system monitoring, energy management, and circuit design.
Principle of Operation:
The wattmeter operates on the principle of calculating power as the product of voltage and current. This is achieved through the sampling, modulation, and processing of voltage and current signals.
1.1 Voltage and Current Signal Sampling:
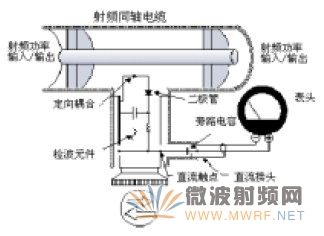
Initially, the wattmeter samples the voltage and current in the circuit. Voltage sensors and current transformers are commonly used to acquire these signals, converting them into measurable analog or digital forms.1.2 Voltage and Current Signal Modulation:
The sampled voltage and current signals undergo modulation for precise power calculation. This modulation process involves steps such as gain amplification, filtering, and linearization to ensure signal accuracy and stability.1.3 Power Calculation and Display:
Following sampling and modulation, the wattmeter utilizes the sampled voltage and current signals to calculate power. It relies on the product of voltage and current, combined with power factor, to derive accurate power values. After calculation, the power values are presented through a display screen or output interface.Technical Parameters:
The wattmeter possesses various technical parameters describing its measurement capabilities and performance characteristics. Common parameters include:
2.1 Accuracy:
Accuracy represents the deviation between the measured results of the wattmeter and the actual values, typically expressed as a percentage or decimal (e.g., ±0.5%).2.2 Frequency Range:
Frequency range indicates the circuit frequency range within which the wattmeter can operate normally. Common frequency ranges include 50 Hz, 60 Hz, and DC.2.3 Power Factor Range:
Power factor range refers to the range of power factors the wattmeter can measure, typically ranging from 0.1 lagging to 1 leading.2.4 Number of Channels:
The number of channels denotes the independent measurement channels the wattmeter has, with options such as single-phase, three-phase, and multiple channels.2.5 Communication Interface:
Wattmeters often come equipped with various communication interfaces, such as RS232, RS485, Ethernet, facilitating data interaction and remote monitoring with other devices.Usage Procedure:
Utilizing the wattmeter involves the following steps:
3.1 Circuit Connection:
Connect appropriate voltage sensors and current transformers to the circuit under test, ensuring correct and secure connections.3.2 Parameter Setting:
Based on measurement requirements, set suitable parameters such as measurement range, power factor, and display units on the wattmeter. Ensure accurate parameter settings.3.3 Initiate Measurement:
Start the wattmeter and observe the measurement results of relevant parameters. Verify the accuracy and stability of measurement values, making necessary calibrations and adjustments.3.4 Data Recording and Analysis:
Optionally, record and save the data measured by the wattmeter for subsequent analysis, report generation, or other purposes.3.5 Troubleshooting and Maintenance:
In case of anomalies or malfunctions during the use of the wattmeter, troubleshoot the issues. Additionally, perform regular maintenance and calibration to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the wattmeter.
In conclusion, the wattmeter serves as a crucial instrument for measuring power in AC circuits. It calculates power based on the product of voltage and current, providing precise measurement results and functionality. The operational principle involves the sampling, modulation, and processing of voltage and current signals. Technical parameters encompass accuracy, frequency range, power factor range, number of channels, and communication interfaces. When using a wattmeter, steps include circuit connection, parameter setting, initiating measurement, data recording and analysis, and troubleshooting. The wattmeter finds extensive application value in power system monitoring, energy management, and circuit design.
相關(guān)討論
推薦內(nèi)容
直播回放: 電機開發(fā)很復(fù)雜?PI MotorXpert?助您事半功倍!
直播回放: ADI 易于驅(qū)動SAR型ADC的原理、優(yōu)點及應(yīng)用介紹
直播回放: 中星聯(lián)華 大咖面對面,輕松玩轉(zhuǎn)高速 ADC 性能測試
AI人工智能深度學(xué)習(xí)(RV1126)-第3期 AI模型部署與項目實戰(zhàn)篇
直播回放: Microchip 利用motorBench?開發(fā)套件高效開發(fā)電機磁場定向控制方案
直播回放: 嵌入式Rust入門基礎(chǔ)知識、解析動手實戰(zhàn)Rust的三個任務(wù)
直播回放: TI 全新推出極具性價比的通用型處理器 AM62L
直播回放: ADI 超低功耗 MCU MAX326xx 系列介紹
直播回放: 2025是德科技數(shù)字月-數(shù)字新品來助陣
直播回放: SiLabs 全新藍牙信道探測:從技術(shù)創(chuàng)新到實際應(yīng)用
直播回放: Fluke 高精度測溫賦能電子制造
直播回放: 節(jié)省至少6個月功能安全認證時長!TI 助力機器人電機控制系統(tǒng)設(shè)計
直播回放: Microchip 多相降壓電源控制技術(shù)的發(fā)展與探討
FPGA Verilog開發(fā)實戰(zhàn)指南——基于Intel Cyclone IV
最優(yōu)化理論與算法(西南科技大學(xué))
設(shè)計示例開箱 - DER-716 - 使用 InnoMux2-EP 的家電 62W 額定三輸出反激電源